반응형
안녕하세요, 이번 포스팅에서는 PyTorch에서 제공하는 VOC Segmentation dataset을 사용해보도록 하겠습니다.
우선 transformation을 정의하기 위한 albumentations 모듈을 설치합니다.
!pip install -U albumentations
필요한 라이브러리를 import 합니다.
from torchvision.datasets import VOCSegmentation
from torchvision.transforms.functional import to_tensor, to_pil_image
from PIL import Image
import torch
import numpy as np
from skimage.segmentation import mark_boundaries
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
from albumentations import HorizontalFlip, Compose, Resize, Normalize
import os
import time
%matplotlib inline
이제, torchvision의 VOCSegmentation 클래스를 사용하여 커스텀 데이터셋을 생성합니다.
# VOCSegmentation dataset을 정의합니다.
class myVOCSegmentation(VOCSegmentation):
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = Image.open(self.images[index]).convert('RGB')
target = Image.open(self.masks[index])
if self.transforms is not None:
augmented = self.transforms(image=np.array(img), mask=np.array(target))
img = augmented['image']
target = augmented['mask']
target[target>20] = 0
img = to_tensor(img)
target = torch.from_numpy(target).type(torch.long)
return img, target
transformation을 정의합니다.
# transformation을 정의합니다.
mean = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
std = [0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
h,w = 520, 520
transform_tran = Compose([Resize(h,w),
HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
Normalize(mean=mean, std=std)])
transform_val = Compose([Resize(h,w),
Normalize(mean=mean, std=std)
])
데이터셋을 저장할 폴더를 생성합니다.
# 데이터셋을 저장할 폴더를 생성합니다.
def createFolder(directory):
try:
if not os.path.exists(directory):
os.makedirs(directory)
except OSError:
print('Error')
createFolder('./data')
myVOCSegmentation dataset을 불러옵니다.
# myVOCSegmentation dataset을 불러옵니다
path2data = './data'
train_ds = myVOCSegmentation(path2data, year='2012', image_set='train', download=True, transforms=transform_tran)
val_ds = myVOCSegmentation(path2data, year='2012', image_set='val', download=True, transforms=transform_val)
print(len(train_ds))
print(len(val_ds))
샘플 이미지를 확인합니다.
# 샘플 이미지를 확인합니다.
np.random.seed(0)
num_classes = 21
COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=(num_classes+1,3), dtype='uint8')
# 이미지와 마스크를 함께 시각화하는 함수를 정의합니다.
def show_img_target(img, target):
if torch.is_tensor(img):
img=to_pil_image(img)
target=target.numpy()
for ll in range(num_classes):
mask=(target==ll)
img=mark_boundaries(np.array(img),mask,outline_color=COLORS[ll],color=COLORS[ll])
plt.imshow(img)
re-normalize 함수를 정의합니다.
# re-normalize 함수를 정의합니다.
def re_normalize(x, mean=mean, std=std):
x_r = x.clone()
for c, (mean_c, std_c) in enumerate(zip(mean,std)):
x_r[c] *= std_c
x_r[c] += mean_c
return x_r
샘플 이미지를 얻습니다.
# 샘플 이미지를 얻습니다.
img, mask = train_ds[6]
print(img.shape, img.type(), torch.max(img))
print(mask.shape, mask.type(), torch.max(mask))
샘플 이미지를 시각화합니다.
# 샘플 이미지를 시각화합니다.
plt.figure(figsize=(20,20))
img_r = re_normalize(img)
plt.subplot(1,3,1)
plt.imshow(to_pil_image(img_r))
plt.subplot(1,3,2)
plt.imshow(mask)
plt.subplot(1,3,3)
show_img_target(img_r, mask)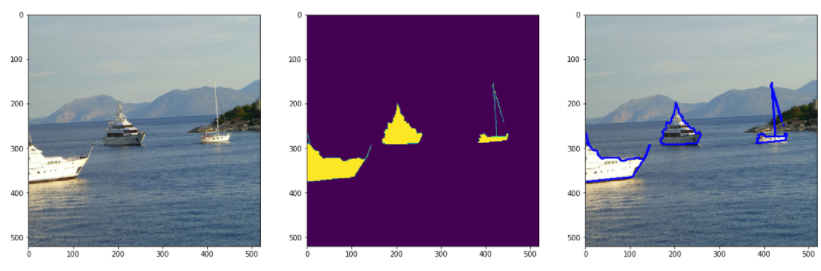
이제 데이터 로더를 생성하고, 모델에 입력해주면 Segmentaion task를 성공적으로 진행할 수 있습니다ㅎㅎ
반응형
'Python > PyTorch 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 이미지 분류 신경망의 결과를 t-SNE 시각화하기 (0) | 2021.07.11 |
|---|---|
| [PyTorch] ShuffleSplit와 subset 함수를 사용하여 dataset 분할하기 (0) | 2021.07.10 |
| [PyTorch] Dice coefficient 을 PyTorch로 구현하기 (3) | 2021.06.25 |
| [PyTorch] to_pil_image 명령어로 tensor를 pil image로 변경하기 (1) | 2021.06.15 |
| [PyTorch] PyTorch에서 제공하는 ResNet을 불러와 마지막 FC layer 수정하기 (0) | 2021.06.12 |