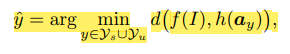Task-Indenpendent Knowledge Makes for Transferable Represenations for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01832
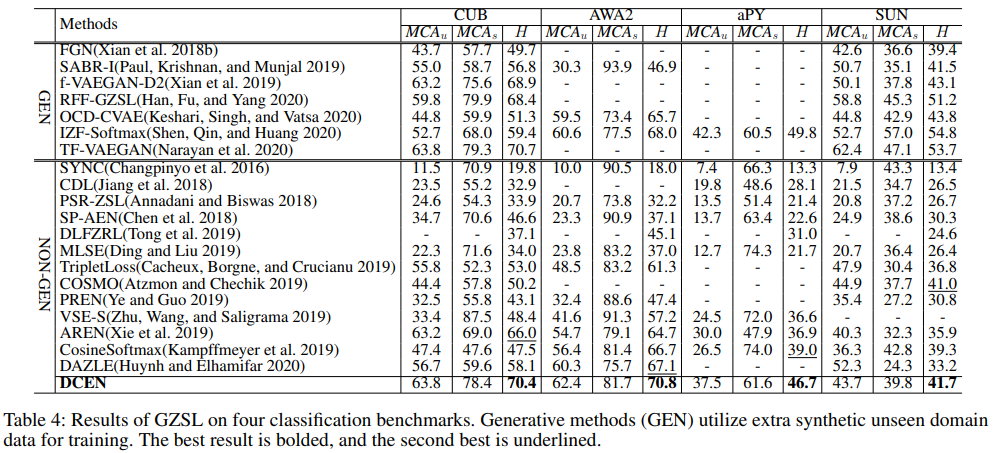
Task-Independent Knowledge Makes for Transferable Representations for Generalized Zero-Shot Learning
Generalized Zero-Shot Learning (GZSL) targets recognizing new categories by learning transferable image representations. Existing methods find that, by aligning image representations with corresponding semantic labels, the semantic-aligned representations
arxiv.org
Zero-Shot Learning은 semantic-visual alignment를 통해 transferable knowledge를 학습시켜 unseen을 예측할 때 이용한다. 이전 방법들은 semantic-visual alignment에 집중을 해왔는데, unseen에 대한 visual feature가 존재하지 않고 seen에 대한 categorie만을 활용하므로 seen bias problem이 존재한다.

논문은 semantic-visual alignment knowledge인 task-specific knowledge와 semantic represenatation에 자유로운 task-independent knowledge를 학습시켜 transferable knowledge를 학습시킨다. task-independent knowledge는 SSL 방식으로 학습되기 때문에 semantic information의 remantic relation에 dependent하다. 따라서 seen의 bias 문제를 완화한다고 설명한다.
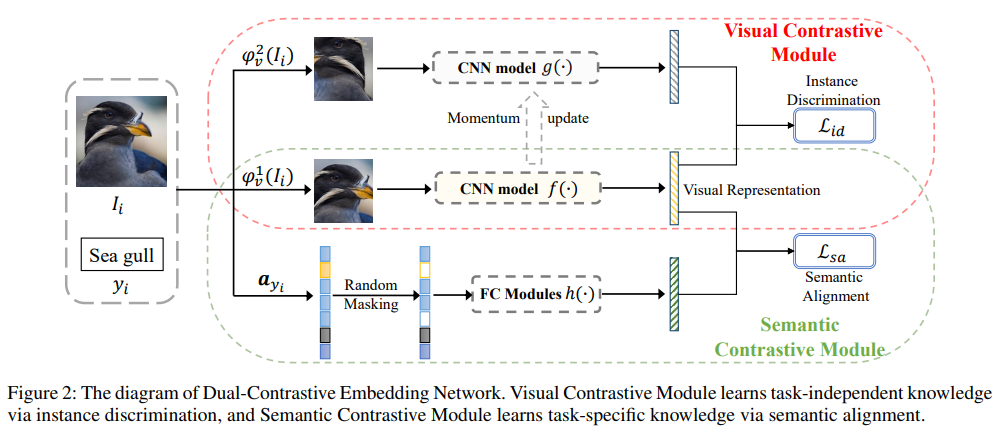
semantic contrastive module과 visual contrastive module로 이루어져 있다.
(1) Semantic Contrastive Module
Semantic Contrastive Module은 attribute를 mask 한다. 입력 noist에 robustness를 향상시키기 위함. 또한 attribute 중에 visual로 판단할 수 없는 abstract semantic information이 존재한다. 이 정보는 visual feature extractor가 추출한 feature로 판별하기가 어렵다. 따라서 masked 된 attribute를 FC layer로 전달해 얻은 출력값과 visual feature 를 align 한다. triplet loss를 사용하는데 가장 헷갈리는 attribute와 discriminative 하기 위함이다.
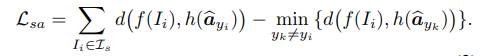
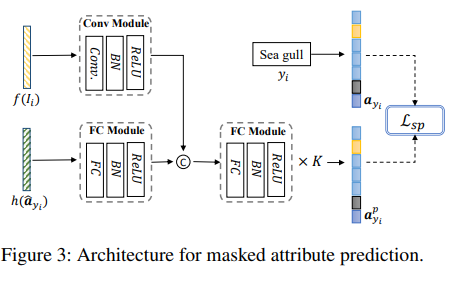
위 loss는 semantic-visual aligment를 위함이었다면, maked atribute를 복원하는 task를 추가하여 visual feature가 semantic information을 포착하도록 한다. masked된 attribute를 복원하려면 attribute에 대한 정보를 visual feature가 잘 알고 있어야 한다.
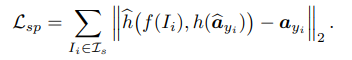
(2) Visual Contrastive Module
VCM은 task-indenpendent한 knowledge를 학습한다. 하나의 이미지에 low-level augmentation을 적용해 두 개의 이미지를 만들고, 가중치를 공유한 샴 네트워크로 전달한다. 동일한 이미지에서 나온 augmentation view는 positive 다른 이미지는 negative로 정의하여 contrastive learning을 수행하여 low-level transformation에 강인한 representation을 추출할 수 있다. 이 represenatation은 semantic information과 무관하므로 seen에 bias 되지 않은 transferable knowledge를 학습한다.
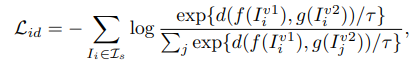
마지막 prediction은 visual space상 distance를 기준으로 수행.