PyTorch Computer Vision Cookbook 을 공부하고 정리한 포스팅입니다.

colab 환경에서 MNIST 데이터를 활용해 간단한 CNN 신경망을 구축하고 학습, 평가까지 진행해 보도록 하겠습니다!
이번 포스팅에서는 다음 순서로 진행됩니다.
- MNIST 데이터셋 불러오고 전처리
- CNN 모델 구축
- loss function과 optimizer 정의
- 학습 및 평가
- 모델 파라미터 저장 및 불러오기
데이터 전처리
우선 구글 colab에 마운트를 해줍니다.
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('cookbook')
CUDA를 확인하고 device를 지정합니다.
import torch
if torch.cuda.is_available():
device = torch.device('cuda:0')
else:
device = torch.device('cpu')
MNIST 데이터셋에 적용할 transformation 객체를 생성합니다.
# define a transformation class in order to apply some image transformation on the MNIST dataset
from torchvision import transforms
# define transformations
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms
MNIST 데이터 셋을 불러오고 transform을 적용합니다.
# load MNIST training dataset
from torchvision import datasets
# path to store data
path2data = './data'
# load training data
train_data = datasets.MNIST(path2data, train=True, download=True, transform=data_transform)
# extract the input data and target labels
x_train, y_train = train_data.data, train_data.targets
# load the MNIST test dataset
# load validation data without data transformation
val_data = datasets.MNIST(path2data, train=False, download=True)
# extract the data and targets
x_val, y_val = val_data.data, val_data.targets
# add a new dimension to the tensors to become B*C*H*W
if len(x_train.shape) == 3:
x_train = x_train.unsqueeze(1) # add one dimension at 1 index
if len(x_val.shape) == 3:
x_val = x_val.unsqueeze(1)
# check a few sample images
from torchvision import utils
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Allows you to view the picture directly from the browser that ran notebook
%matplotlib inline
# define a helper function to display tensors as images
def show(img):
# convert tensor to numpy array
npimg = img.numpy()
# convert to H*W*C shape from C*H*W
npimg_tr = npimg.transpose((1,2,0))
plt.imshow(npimg_tr, interpolation='nearest')
# create a grid of images and display them
# make a grid of 40 images, 8 images per row
x_grid = utils.make_grid(x_train[:40], nrow=8, padding=2) # padding means edge pixel
# call helper function
show(x_grid)

transform이 적용되었나 확인합니다.
# check transpose
img = train_data[0][0]
img_np = img.numpy().squeeze(0)
plt.imshow(img_np,cmap='gray')
plt.title('transpose')

tensors를 dataset으로 감쌉니다.
# create a PyTorch dataset by wrapping x_train and y_train
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
# wrap tensors into a dataset
train_ds = TensorDataset(x_train, y_train)
val_ds = TensorDataset(x_val, y_val)
data loader를 생성합니다.
# create two data loaders for the training and validaiton datasets
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
# create a data loader from dataset
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=8)
val_dl = DataLoader(val_ds, batch_size=8)
이제 데이터 전처리가 끝났습니다!
모델을 구축해보도록 하겠습니다.
모델 구축
nn.Module을 사용해 모델을 정의합니다.
여기서는 2개 convolutional layer와 2개 fully connected layer를 활용했습니다.
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5, 1) # input, output, kernel_size, stride
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 50, 5, 1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4*4*50, 500)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2, 2)
x = x.view(-1, 4*4*50)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
model = Net()
모델을 CUDA device로 전달합니다.
# move the model to the CUDA device
model.to(device)
모델 요약본을 출력합니다.
from torchsummary import summary
summary(model, input_size=(1, 28, 28))
모델이 성공적으로 구축되었습니다!
Loss function과 optimizer 정의하고 학습하기
loss function과 optimizer를 정의합니다.
from torch import nn
from torch import optim
# define the negative log-likelihood loss
loss_func = nn.NLLLoss(reduction='sum')
# define the Adam optimizer
opt = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
학습을 위한 helper function을 정의합니다.
# define a helper function to compute the loss value per mini-batch
def loss_batch(loss_func, xb, yb, yb_h, opt=None):
# obtain loss
loss = loss_func(yb_h, yb)
# obtain performance metric
metric_b = metrics_batch(yb, yb_h)
if opt is not None:
loss.backward() # compute gradient
opt.step() # update parameters
opt.zero_grad() # set gradients to zero
return loss.item(), metric_b
# define a helper function to compute the accurary per mini-batch
def metrics_batch(target, output):
# optain output class
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True)
# compare output class with target class
corrects = pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
return corrects
# define a helper fuction to compute the loss and metric values for a dataset
def loss_epoch(model, loss_func, dataset_dl, opt=None):
loss = 0.0
metric = 0.0
len_data = len(dataset_dl.dataset)
for xb, yb in dataset_dl:
xb = xb.type(torch.float).to(device)
yb = yb.to(device)
# obtain model output
yb_h = model(xb)
loss_b, metric_b = loss_batch(loss_func, xb, yb, yb_h, opt)
loss += loss_b
if metric_b is not None:
metric += metric_b
loss /= len_data
metric /= len_data
return loss, metric
학습하는 함수를 정의합니다.
# define train_val function
def train_val(epochs, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, val_dl):
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train() # convert to train mode
train_loss, train_metric = loss_epoch(model, loss_func, train_dl, opt)
model.eval() # convert to evaluation mode
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss, val_metric = loss_epoch(model, loss_func, val_dl)
accuracy = 100 * val_metric
print('epoch: %d, train loss: %.6f, val loss: %.6f, accuracy: %.2f' %(epoch, train_loss, val_loss, accuracy))
학습을 해보겠습니다.
# train model for a few epochs
# call train_val function
num_epochs = 5
train_val(num_epochs, model, loss_func, opt, train_dl, val_dl)

모델 저장하고 불러오기
학습된 모델의 가중치를 저장하고 불러오겠습니다.
방법은 두 가지가 있습니다.
방법 1: 모델의 파라미터를 저장하고 파라미터를 불러오기
# store the model parameters or state_dict in a file
# define path2weights
path2weights = './models/weight.pt'
# check directory
import os
def createFolder(directory):
try:
if not os.path.exists(directory):
os.makedirs(directory)
except OSerror:
print('Error')
createFolder('./models')
# store state_dict to file
torch.save(model.state_dict(), path2weights)
# definc model : weights are randomly initiated
_model = Net()
# load weights from file
weights = torch.load(path2weights)
# set weights to model : weights are set with the stored values
_model.load_state_dict(weights)
방법 2: 모델을 저장하고 불러오기
# store the model in a file
# define a path2model
path2model = './models/model.pt'
# check directory
import os
def createFolder(directory):
try:
if not os.path.exists(directory):
os.makedirs(directory)
except OSerror:
print('Error')
createFolder('./models')
# store model and weights into a file
torch.save(model, path2model)
# define model : weights are randomly initiated
_model = Net()
# load the model from the local file
_model = torch.load(path2model)
추론하기
학습이 잘 되었는지 확인하기 위해 학습된 모델을 validation 데이터로 추론을 해보겠습니다.
# pass new data to the model
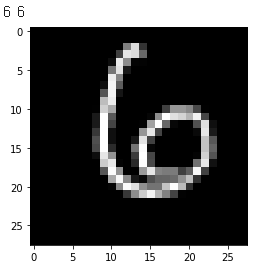
# To inference the model on a sample image from the validation dataset, get a sample data
n = 100
x = x_val[n]
y = y_val[n]
plt.imshow(x.numpy()[0],cmap='gray')
# use unsqueeze to expand dimensions to 1*C*H*W
x = x.unsqueeze(0)
# convert the type to torch.float32
x = x.type(torch.float)
# move to cuda device
x = x.to(device)
# get the model prediction
output = _model(x)
# get predicted class
pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True)
print(pred.item(), y.item())
'Python > PyTorch 공부' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [PyTorch] convolutional layer 출력 크기 계산하는 함수 만들기 (0) | 2021.02.22 |
|---|---|
| [PyTorch] 암 이미지로 커스텀 데이터셋 만들기(creating custom dataset for cancer images) (0) | 2021.02.22 |
| [Object Detection] YOLO(v3)를 PyTorch로 바닥부터 구현하기 - Part 5 (0) | 2021.01.31 |
| [Object Detection] YOLO(v3)를 PyTorch로 바닥부터 구현하기 - Part 4 (0) | 2021.01.29 |
| [Object Detection] YOLO(v3)를 PyTorch로 바닥부터 구현하기 - Part 3 (6) | 2021.01.25 |