이번 포스팅에서는 DCGAN을 PyTorch로 구현하고, STL-10 dataset으로 학습을 시킨 후에 학습된 generator이 생성한 가짜 이미지를 확인해보겠습니다.
논문 리뷰는 아래 포스팅에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
[논문 읽기] 구현 코드로 살펴보는 DCGAN(2015), Deep Convolutional Generative adversatial networks
오늘 읽은 논문은 DCGAN, Unsupervised Representation Learning with Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks 입니다. DCGAN은 generator와 discriminator 구조에 CNN을 적용한 것입니다. 이미지..
deep-learning-study.tistory.com
전체 코드는 아래 깃허브에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
Seonghoon-Yu/Paper_Review_and_Implementation_in_PyTorch
공부 목적으로 논문을 리뷰하고 파이토치로 구현하고 있습니다. Contribute to Seonghoon-Yu/Paper_Review_and_Implementation_in_PyTorch development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
우선, 라이브러리를 불러옵니다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms.functional import to_pil_image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
import time
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
1. STL-10 dataset 데이터셋 불러오기
# 데이터 경로 지정
path2data = './data'
os.makedirs(path2data, exist_ok=True)
# transforms 정의하기
h, w = 64, 64
mean = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
std = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((h,w)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean, std)
])
STL-10 dataset을 불러옵니다.
# STL-10 dataset 불러오기
train_ds = datasets.STL10(path2data, split='train', download=True, transform=transform)
샘플 이미지를 확인합니다.
# 샘플 이미지 확인
img, label = train_ds[0]
plt.imshow(to_pil_image(0.5*img+0.5))
# DataLoader 생성하기
batch_size = 64
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
2. 모델 구축하기
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/dcgan_faces_tutorial.html 코드를 참고해서 구현했습니다.
# 파라미터 정의
params = {'nz':100, # noise 수
'ngf':64, # generator에서 사용하는 conv filter 수
'ndf':64, # discriminator에서 사용하는 conv filter 수
'img_channel':3, # 이미지 채널
}
Generator을 구현합니다.
# Generator: noise를 입력받아 가짜 이미지를 생성합니다.
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, params):
super().__init__()
nz = params['nz'] # noise 수, 100
ngf = params['ngf'] # conv filter 수
img_channel = params['img_channel'] # 이미지 채널
self.dconv1 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(nz,ngf*8,4, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf*8)
self.dconv2 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf*8,ngf*4, 4, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf*4)
self.dconv3 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf*4,ngf*2,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf*2)
self.dconv4 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf*2,ngf,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf)
self.dconv5 = nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf,img_channel,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
def forward(self,x):
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.dconv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.dconv2(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.dconv3(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.dconv4(x)))
x = torch.tanh(self.dconv5(x))
return x
# check
x = torch.randn(1,100,1,1, device=device)
model_gen = Generator(params).to(device)
out_gen = model_gen(x)
print(out_gen.shape)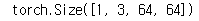
Discriminator을 구현합니다.
# Discriminator: 진짜 이미지와 가짜 이미지를 식별합니다.
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,params):
super().__init__()
img_channel = params['img_channel'] # 3
ndf = params['ndf'] # 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(img_channel,ndf,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(ndf,ndf*2,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf*2)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(ndf*2,ndf*4,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf*4)
self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(ndf*4,ndf*8,4,stride=2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf*8)
self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(ndf*8,1,4,stride=1,padding=0,bias=False)
def forward(self,x):
x = F.leaky_relu(self.conv1(x),0.2)
x = F.leaky_relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)),0.2)
x = F.leaky_relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x)),0.2)
x = F.leaky_relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(x)),0.2)
x = torch.sigmoid(self.conv5(x))
return x.view(-1,1)
# check
x = torch.randn(16,3,64,64,device=device)
model_dis = Discriminator(params).to(device)
out_dis = model_dis(x)
print(out_dis.shape)
가중치를 초기화합니다.
# 가중치 초기화
def initialize_weights(model):
classname = model.__class__.__name__
if classname.find('Conv') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(model.bias.data, 0)
# 가중치 초기화 적용
model_gen.apply(initialize_weights);
model_dis.apply(initialize_weights);
3. 학습하기
# 손실 함수 정의
loss_func = nn.BCELoss()
# 최적화 함수
from torch import optim
lr = 2e-4
beta1 = 0.5
beta2 = 0.999
opt_dis = optim.Adam(model_dis.parameters(),lr=lr,betas=(beta1,beta2))
opt_gen = optim.Adam(model_gen.parameters(),lr=lr,betas=(beta1,beta2))
100epoch 학습을 진행하겠습니다.
model_gen.train()
model_dis.train()
batch_count=0
num_epochs=100
start_time = time.time()
nz = params['nz'] # 노이즈 수 100
loss_hist = {'dis':[],
'gen':[]}
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for xb, yb in train_dl:
ba_si = xb.shape[0]
xb = xb.to(device)
yb_real = torch.Tensor(ba_si,1).fill_(1.0).to(device)
yb_fake = torch.Tensor(ba_si,1).fill_(0.0).to(device)
# generator
model_gen.zero_grad()
z = torch.randn(ba_si,nz,1,1).to(device) # noise
out_gen = model_gen(z) # 가짜 이미지 생성
out_dis = model_dis(out_gen) # 가짜 이미지 식별
g_loss = loss_func(out_dis,yb_real)
g_loss.backward()
opt_gen.step()
# discriminator
model_dis.zero_grad()
out_dis = model_dis(xb) # 진짜 이미지 식별
loss_real = loss_func(out_dis,yb_real)
out_dis = model_dis(out_gen.detach()) # 가짜 이미지 식별
loss_fake = loss_func(out_dis,yb_fake)
d_loss = (loss_real + loss_fake) / 2
d_loss.backward()
opt_dis.step()
loss_hist['gen'].append(g_loss.item())
loss_hist['dis'].append(d_loss.item())
batch_count += 1
if batch_count % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch: %.0f, G_Loss: %.6f, D_Loss: %.6f, time: %.2f min' %(epoch, g_loss.item(), d_loss.item(), (time.time()-start_time)/60))
loss history를 출력합니다.
# loss history
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.title('Loss Progress')
plt.plot(loss_hist['gen'], label='Gen. Loss')
plt.plot(loss_hist['dis'], label='Dis. Loss')
plt.xlabel('batch count')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
학습된 가중치를 저장합니다.
# 가중치 저장
path2models = './models/'
os.makedirs(path2models, exist_ok=True)
path2weights_gen = os.path.join(path2models, 'weights_gen.pt')
path2weights_dis = os.path.join(path2models, 'weights_dis.pt')
torch.save(model_gen.state_dict(), path2weights_gen)
torch.save(model_dis.state_dict(), path2weights_dis)
4. Generator이 생성한 가짜 이미지 확인하기
학습된 가중치를 불러옵니다.
# 가중치 불러오기
weights = torch.load(path2weights_gen)
model_gen.load_state_dict(weights)
가짜 이미지를 생성합니다.
# evalutaion mode
model_gen.eval()
# fake image 생성
with torch.no_grad():
fixed_noise = torch.randn(16, 100,1,1, device=device)
label = torch.randint(0,10,(16,), device=device)
img_fake = model_gen(fixed_noise).detach().cpu()
print(img_fake.shape)
가짜 이미지를 시각화합니다.
# 가짜 이미지 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for ii in range(16):
plt.subplot(4,4,ii+1)
plt.imshow(to_pil_image(0.5*img_fake[ii]+0.5), cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
형체를 알아볼 수 있는 이미지를 생성했네요..ㅎㅎ 학습이 더 필요합니다!
'논문 구현' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 Style Transfer(2015)를 구현하고 학습하기 (0) | 2021.06.11 |
|---|---|
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 Pix2Pix(2016) 구현하고 학습하기 (5) | 2021.05.20 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 CGAN(2014) 구현하고 학습하기 (1) | 2021.05.18 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 GAN(2014) 구현하고 학습하기 (3) | 2021.05.17 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 RetinaNet(2017) 구현하고 학습하기 (2) | 2021.05.06 |