안녕하세요, 이번 포스팅에서는 PyTorch로 Knowledge Distillation을 구현해보도록 하겠습니다. 작업 환경은 Google Colab에서 진행했습니다.
논문 리뷰는 아래 포스팅에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
[논문 읽기] PyTorch 구현 코드로 살펴보는 Knowledge Distillation(2014), Distilling the Knowledge in Neural Network
안녕하세요, 오늘 읽은 논문은 Distilling the Knoeledge in a Neural Network 입니다. 해당 논문은 Knowledge Distillation을 제안합니다. Knowledge Distillation은 teacher model이 갖고 있는 지식을 더 작..
deep-learning-study.tistory.com
전체 코드는 아래 깃허브에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
Seonghoon-Yu/Paper_Review_and_Implementation_in_PyTorch
공부 목적으로 논문을 리뷰하고 해당 논문 파이토치 재구현을 합니다. Contribute to Seonghoon-Yu/Paper_Review_and_Implementation_in_PyTorch development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
우선 필요한 라이브러리를 import 합니다.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import torchvision.models as models
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import time
import os
import copy
from torchvision.transforms.functional import to_pil_image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
Loading MNIST dataset
MNIST dataset을 불러옵니다.
# make directorch to save dataset
def createFolder(directory):
try:
if not os.path.exists(directory):
os.makedirs(directory)
except OSerror:
print('Error')
createFolder('./data')
# define transformation
ds_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,),(0.3081,))
])
dataset을 생성합니다
# load MNIST dataset
train_ds = datasets.MNIST('/content/data',train=True, download=True, transform=ds_transform)
val_ds = datasets.MNIST('/content/data',train=False, download=True, transform=ds_transform)
데이터 로더를 생성합니다.
# define data loader
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
val_dl = DataLoader(val_ds, batch_size = 128, shuffle=True)
샘플 이미지를 확인합니다.
# check sample image
for x, y in train_dl:
print(x.shape, y.shape)
break
num = 4
img = x[:num]
plt.figure(figsize=(15,15))
for i in range(num):
plt.subplot(1,num+1,i+1)
plt.imshow(to_pil_image(0.1307*img[i]+0.3081), cmap='gray')
Define Teacher model
Knowledge distillation을 하기 위해서 soft label을 얻기 위한 teacher model을 먼저 학습해야 합니다. 따라서 teacher model을 정의합니다.
class Teacher(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 1200)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1200)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(1200,1200)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1200)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(1200, 10)
def forward(self,x):
x = x.view(-1, 28*28)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.fc1(x)))
x = F.dropout(x,p=0.8)
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.fc2(x)))
x = F.dropout(x,p=0.8)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# check
x = torch.randn(16,1,28,28).to(device)
teacher = Teacher().to(device)
output = teacher(x)
print(output.shape)
가중치를 초기화합니다.
# weight initialization
def initialize_weights(model):
classname = model.__class__.__name__
# fc layer
if classname.find('Linear') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(model.bias.data, 0)
# batchnorm
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(model.bias.data, 0)
teacher.apply(initialize_weights);
Train teacher model
teacher model을 학습합니다.
# loss function
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# optimizer
opt = optim.Adam(teacher.parameters())
# lr scheduler
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import ReduceLROnPlateau
lr_scheduler = ReduceLROnPlateau(opt, mode='min', factor=0.1, patience=10)
# get current lr
def get_lr(opt):
for param_group in opt.param_groups:
return param_group['lr']
# calculate the metric per mini-batch
def metric_batch(output, target):
pred = output.argmax(1, keepdim=True)
corrects = pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
return corrects
# calculate the loss per mini-batch
def loss_batch(loss_func, output, target, opt=None):
loss_b = loss_func(output, target)
metric_b = metric_batch(output, target)
if opt is not None:
opt.zero_grad()
loss_b.backward()
opt.step()
return loss_b.item(), metric_b
# calculate the loss per epochs
def loss_epoch(model, loss_func, dataset_dl, sanity_check=False, opt=None):
running_loss = 0.0
running_metric = 0.0
len_data = len(dataset_dl.dataset)
for xb, yb in dataset_dl:
xb = xb.to(device)
yb = yb.to(device)
output = model(xb)
loss_b, metric_b = loss_batch(loss_func, output, yb, opt)
running_loss += loss_b
if metric_b is not None:
running_metric += metric_b
if sanity_check is True:
break
loss = running_loss / len_data
metric = running_metric / len_data
return loss, metric
# function to start training
def train_val(model, params):
num_epochs=params['num_epochs']
loss_func=params['loss_func']
opt=params['optimizer']
train_dl=params['train_dl']
val_dl=params['val_dl']
sanity_check=params['sanity_check']
lr_scheduler=params['lr_scheduler']
path2weights=params['path2weights']
loss_history = {'train': [], 'val': []}
metric_history = {'train': [], 'val': []}
best_loss = float('inf')
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
current_lr = get_lr(opt)
print('Epoch {}/{}, current lr= {}'.format(epoch, num_epochs-1, current_lr))
model.train()
train_loss, train_metric = loss_epoch(model, loss_func, train_dl, sanity_check, opt)
loss_history['train'].append(train_loss)
metric_history['train'].append(train_metric)
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss, val_metric = loss_epoch(model, loss_func, val_dl, sanity_check)
loss_history['val'].append(val_loss)
metric_history['val'].append(val_metric)
if val_loss < best_loss:
best_loss = val_loss
best_model_wts = copy.deepcopy(model.state_dict())
torch.save(model.state_dict(), path2weights)
print('Copied best model weights!')
lr_scheduler.step(val_loss)
if current_lr != get_lr(opt):
print('Loading best model weights!')
model.load_state_dict(best_model_wts)
print('train loss: %.6f, val loss: %.6f, accuracy: %.2f, time: %.4f min' %(train_loss, val_loss, 100*val_metric, (time.time()-start_time)/60))
print('-'*10)
model.load_state_dict(best_model_wts)
return model, loss_history, metric_history
# set hyper parameters
params_train = {
'num_epochs':30,
'optimizer':opt,
'loss_func':loss_func,
'train_dl':train_dl,
'val_dl':val_dl,
'sanity_check':False,
'lr_scheduler':lr_scheduler,
'path2weights':'./models/teacher_weights.pt',
}
createFolder('./models')
30 epoch 학습하겠습니다.
teacher, loss_hist, metric_hist = train_val(teacher, params_train)
loss와 accuracy를 시각화합니다.
num_epochs = params_train['num_epochs']
# Plot train-val loss
plt.title('Train-Val Loss')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), loss_hist['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), loss_hist['val'], label='val')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Training Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# plot train-val accuracy
plt.title('Train-Val Accuracy')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), metric_hist['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), metric_hist['val'], label='val')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Training Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()

Define Student model
이제 teacher의 지식을 transfer할 student model을 정의합니다.
class Student(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28*28, 800)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(800)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(800,800)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(800)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(800,10)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 28*28)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.fc1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# check
x = torch.randn(16,1,28,28).to(device)
student = Student().to(device)
output = student(x)
print(output.shape)
가중치를 초기화합니다.
# weight initialization
def initialize_weights(model):
classname = model.__class__.__name__
# fc layer
if classname.find('Linear') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 0.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(model.bias.data, 0)
# batchnorm
elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
nn.init.normal_(model.weight.data, 1.0, 0.02)
nn.init.constant_(model.bias.data, 0)
student.apply(initialize_weights);
Knowledge distillation
이제 teacher model의 soft label을 사용하여 student model을 knowledge distillation loss로 학습하겠습니다.
teacher = Teacher().to(device)
# load weight
teacher.load_state_dict(torch.load('/content/models/teacher_weights.pt'))
student = Student().to(device)
# optimizer
opt = optim.Adam(student.parameters())
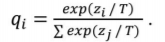

# knowledge distillation loss
def distillation(y, labels, teacher_scores, T, alpha):
# distillation loss + classification loss
# y: student
# labels: hard label
# teacher_scores: soft label
return nn.KLDivLoss()(F.log_softmax(y/T), F.softmax(teacher_scores/T)) * (T*T * 2.0 + alpha) + F.cross_entropy(y,labels) * (1.-alpha)
# val loss
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
def distill_loss_batch(output, target, teacher_output, loss_fn=distillation, opt=opt):
loss_b = loss_fn(output, target, teacher_output, T=20.0, alpha=0.7)
metric_b = metric_batch(output, target)
if opt is not None:
opt.zero_grad()
loss_b.backward()
opt.step()
return loss_b.item(), metric_b
100epoch 학습하겠습니다.
num_epochs= 100
loss_history = {'train': [], 'val': []}
metric_history = {'train': [], 'val': []}
best_loss = float('inf')
start_time = time.time()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
current_lr = get_lr(opt)
print('Epoch {}/{}, current lr= {}'.format(epoch, num_epochs-1, current_lr))
# train
student.train()
running_loss = 0.0
running_metric = 0.0
len_data = len(train_dl.dataset)
for xb, yb in train_dl:
xb = xb.to(device)
yb = yb.to(device)
output = student(xb)
teacher_output = teacher(xb).detach()
loss_b, metric_b = distill_loss_batch(output, yb, teacher_output, loss_fn=distillation, opt=opt)
running_loss += loss_b
running_metric_b = metric_b
train_loss = running_loss / len_data
train_metric = running_metric / len_data
loss_history['train'].append(train_loss)
metric_history['train'].append(train_metric)
# validation
student.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
val_loss, val_metric = loss_epoch(student, loss_func, val_dl)
loss_history['val'].append(val_loss)
metric_history['val'].append(val_metric)
lr_scheduler.step(val_loss)
print('train loss: %.6f, val loss: %.6f, accuracy: %.2f, time: %.4f min' %(train_loss, val_loss, 100*val_metric, (time.time()-start_time)/60))
print('-'*10)
teacher model보다 accuracy가 2% 향상되었습니다 ㅎㅎ!!
loss와 accuracy를 시각화합니다.
# Plot train-val loss
plt.title('Train-Val Loss')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), loss_hist['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), loss_hist['val'], label='val')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.xlabel('Training Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
# plot train-val accuracy
plt.title('Train-Val Accuracy')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), metric_hist['train'], label='train')
plt.plot(range(1, num_epochs+1), metric_hist['val'], label='val')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Training Epochs')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
Reference
- https://github.com/peterliht/knowledge-distillation-pytorch
- https://baeseongsu.github.io/posts/knowledge-distillation/#q3-knowledge-distillation%EC%9D%80-%EC%96%B4%EB%96%BB%EA%B2%8C-%ED%95%98%EB%8A%94-%EA%B1%B8%EA%B9%8C-with-hintons-kd
- http://cs230.stanford.edu/files_winter_2018/projects/6940224.pdf
'논문 구현' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [논문 구현] ViT(2020) PyTorch 구현 및 학습 (3) | 2021.08.04 |
|---|---|
| [논문 구현] MoCov2(2020) PyTorch 구현 (1) | 2021.07.12 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 SRCNN(2014) 구현하고 학습하기 (3) | 2021.06.15 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 Seq2Seq(2014) 구현하고 학습하기 (0) | 2021.06.15 |
| [논문 구현] PyTorch로 Style Transfer(2015)를 구현하고 학습하기 (0) | 2021.06.11 |